Protecting Sensitive Records Through Encrypted Data Rooms
Encrypted Data Clean Room from SafeLiShare
The need for organizations to protect sensitive records from unauthorized access and potential exploitation is greater than ever before. If you are a customer, you need to insist on control over where your data resides, and who has access to it, every step of the way from data at rest, in transit to in use. One of the most effective ways to ensure data privacy and security is by using encrypted rooms or data clean rooms for storing, sharing, and recovering confidential information as you bring “compute to data” or “data to compute.” In this article, we will discuss how organizations can take advantage of encrypted rooms to protect sensitive records in the context of confidential computing.
Businesses are attempting to use privacy-enhancing technology, as well as other solutions like robotic process automation (RPA) or ransomware tools, to identify and mitigate attack threats as the cost of a data breach rises along with the frequency of cyberattacks detected daily. However, this is ineffective if your data is not encrypted and the communication method is not secure. As technology becomes more prevalent, organizations must face the challenge of protecting sensitive records and data from unauthorized access. Organizations handle a variety of confidential records and data for their clients. Security measures must be taken to prevent unauthorized access to this information. Data encryption is used to protect data from prying eyes and malicious actors.
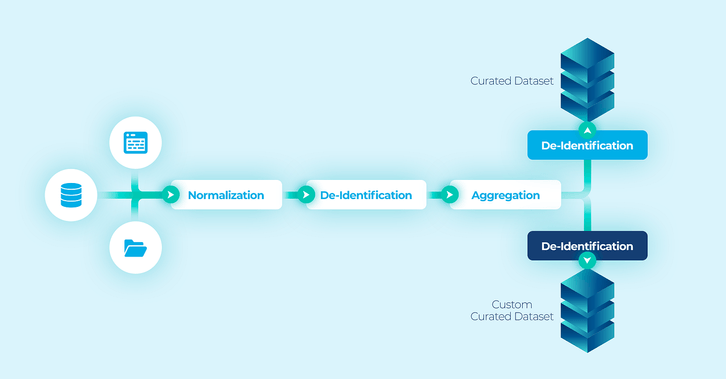
Encrypted rooms provide extra security for sensitive documents stored digitally by protecting the information both at a physical level and online. These data encryption rooms are used as secure storage enclaves to keep your data safe from unwanted access and potential breaches. The keys to these storage enclaves are managed and protected using confidential computing technologies. Data encryption rooms keep all of your sensitive data and code assets safe whether you bring the “compute to data” or vice versa, and transparently secure the workloads.
Owners of encrypted clean rooms may define a “federation” into which they may share, using authorization policies, their code, and data assets. Federations are logical structures holding registrations (meta-data) of shared assets. Each federation structure has a browsable catalog of all assets shared in the federation. Shared federated assets may then be combined into executable workloads by authorized users, accounts, and organizations.
SafeLiShare’s innovative encryption methodology protects code and data assets at all stages of workflows. At each stage, a workload may be defined by an authorized user by combining assets shared into a federation by the asset owners. The resulting workload is then executed using SafeLiShare technology ensuring all policies are satisfied and complied with. Using shared assets leads to the creation of customized insights and results. Securing data and code sharing is an essential tool for businesses that need to protect sensitive information without compromising productivity.
SafeLiShare uses recent advances in confidential computing technology to provide Policy Driven Access to Applications and Data (PDAAD) throughout the entire workflow. Support for audit and verification functionality is now possible with SafeLiShare’s PDAAD technology.
Multi-Party Confidential Computation with Distributed Access Control
Data Security and Compliance Challenge
This misconception that regulatory compliance equates to security is a mistake that enterprises frequently make. Your sensitive data must be secured in accordance with HIPAA, PII, PCI, CJIS, and other legal requirements. However, they don’t go into great depth on how you should go about doing it. Some exclude any mention of encryption entirely.
These legal requirements hold your hand to ensure that you get data secured properly because there are many different ways to get it wrong. Even worse, after they accomplish the bare minimum security required for a regulatory checkmark, many development teams who add encryption to their code give up. This emphasis on data security as a “checkmark” is dangerous.
Robust cybersecurity is becoming more and more important as complexity rises. A large majority of respondents (66%) indicated that between 21 and 60% of their sensitive data is kept in the cloud. Only 25% of participants, however, claimed to be able to completely classify all data.
In addition, over a third (32%) of respondents acknowledged that they had to notify a government agency, client, business partner, or employee of a breach. Enterprises with sensitive data should be concerned about this, especially those in industries with strict regulations.
Organizations potentially lose millions of dollars as a result of costly data breaches that result in lost revenue. Following a data or security breach, organizations not only have internal issues but also suffer a loss of customer trust. Research by Okta and YouGov found that 39% of consumers said they stopped doing business with a firm after learning of a data breach or data misuse. 88 percent of people said they won’t make a purchase from a company they don’t believe in. Data encryption is necessary in order to prevent the consequences of a security and data breach.
For cloud apps and data, cyberattacks pose a persistent danger. One-fifth (19%) of respondents said they had seen a rise in phishing/whaling, while a quarter (26%) mentioned an increase in malware and a quarter (25%) in ransomware.
The most recent Uber hack serves as more proof that individuals and easily available data are always the weakest link and will thus always be taken advantage of. It also serves as a reminder that even organizations with excellent intentions and cutting-edge technologies can run into serious problems. In order to access Uber’s VPN and scan the network, the attacker discovered a PowerShell script that had the hardcoded administrator user credentials. Using these credentials, the attacker was able to obtain access to all of Uber’s internal cloud and software-as-a-service resources. This demonstrates that the data was presented in hard-coded form, making it simple and feasible for an attacker to exploit. Attackers were able to access names, email addresses, and phone numbers from 57 million Uber accounts throughout the world. Additionally, 7 million drivers, including information from over 600,000 driver’s licenses, were impacted.
Encrypted Data Platform
Digital data is continuously shared and stored in the cloud and on associated services. The average cost of a data breach involving 50 million to 65 million records, according to IBM, is more than $400 million. SafeLiShare supports encrypted data clean rooms in which the data and application sharing policies and governance rules — the terms and conditions governing the clean room — are stated by the asset owners, not the clean room provider. Using PDAAD, all application access to data in a clean room is auditable, trackable, and visible. PDAAD also enforces governance and ownership policies stated by the respective asset owners. Audit logs are made available for verification of operations and access to data in the clean room. All registered data and applications are provided to a clean room in encrypted form.
Traditional encryption is only useful while data is at rest (disk encryption) or in transit using secure communication protocols like SSL and TLS. However, if the attacker has the user credentials, the data will be provided to the attacker after being decrypted if the attacker appears to have access permissions. The distinction is that when data is accessed through a query, it is no longer “at rest” or “in transit,” but rather it is “in use,” and conventional encryption doesn’t secure data in use. Major data security breaches, like the 2022 Cash App Breach when a former employee with user credentials was able to breach the servers, frequently include the theft of passwords and accessing data through searches.
SafeLiShare encrypted data clean rooms are, in essence, a series of interconnected secure enclaves based on confidential computing technology, that control and manage the keys used to decrypt the registered assets and control the ensuing computations. End-to-end protection for sensitive and private information brought into the clean room is ensured as assets are re-encrypted when exiting the data clean room
In an era when data has become the product for many enterprises and faces increased scrutiny due to tightening global regulations, SafeLiShare was founded with a vision to provide application-specific access to data, enabling new business models and revenue streams for all data. All operations on data by applications are made visible, auditable, and trackable so usability and productivity will increase along with data security.
Dependency on Third-Party Vendors
The majority of vendors who provide encryption products and EKM solutions do not enable the use of third-party EKM for encryption keys. Despite third-party compliance with the OASIS KMIP standard, this remains the case. Most solutions are unable to obtain a single cryptographic solution that can meet all of their cryptographic standards. Many use cases that need encryption, such as data protection at rest, SSL/TLS, and SSH, can be included. An application running in a secure enclave is isolated because no other application can access its encrypted memory space.
The most challenging aspect of any third-party cryptography deployment is understanding the numerous vendor configurations, system parameters, platform requirements, and system constraints connected with a cryptographic solution. The number of various manufacturers’ cryptographic solutions implemented inside a particular environment raises the overall complexity level of the system.
SafeLiShare Confidential Computing technology allows the creation of run-time environments, called secure enclaves, that assign encrypted memory space to user applications. Confidential computing hardware protects the keys used to decrypt the encrypted memory space assigned to applications. The data being processed by an application running in a secure enclave, and the code of the application, is protected from other applications that may be running on the same computer. Before providing a data decryption key to an application, the secure enclave in which the application is running is required to “attest” itself to the satisfaction of the policy server. Attestation services are provided by the hardware manufacturer and, more recently, by infrastructure providers.

Encrypted Data Clean Room by SafeLiShare
Summary
SafeLiShare uses infrastructure services running in secure enclaves to generate encryption keys that may be used by data and application owners to encrypt their data and applications. The corresponding decryption keys are only made available by the policy server to applications inside a secure enclave.
The key to keeping your data secure is to develop risk-based data security practices. You may improve data security and compliance by identifying and categorizing your data, analyzing and managing IT risks, and implementing suitable controls.
Consider starting with a best-practice framework, such as the NIST CSF, and then looking for security solutions that will assist you in automating essential operations and providing the necessary information. Remember that data security is a continuous activity, not a one-time event. Despite the fact that data privacy regulations such as GDPR in the EU and CCPA in California are intended to prevent privacy breaches, hackers, companies, and governments often invade consumers’ privacy.
Managing and granting access to these applications becomes the responsibility of the various data domains. PDAAD gives explicit recognition to data and application ownership. Data may only become accessible to authorized applications and such authorizations are granted by the data owners. At the same time, PDAAD ensures that application owners permit their applications to process specific datasets. Such symmetric authorizations are at the heart of PDAAD.
SafeLiShare is fundamentally redefining today’s data and application infrastructures to provide complete control over data residency, sovereignty, and compliance. Customer data is transparently encrypted at rest, in transit, and in use (during execution), so workloads stay confidential and trusted end-to-end. Components of workloads (e.g., data and code assets) may be shared securely with partners with IP and data protection. For more information or to schedule a demo, visit here.
Suggested for you
February 21, 2024
RSAC 2024: What’s New
SafeLiShare unveils groundbreaking AI-powered solutions: the AI Sandbox and Privacy Guard in RSAC 2024
February 21, 2024
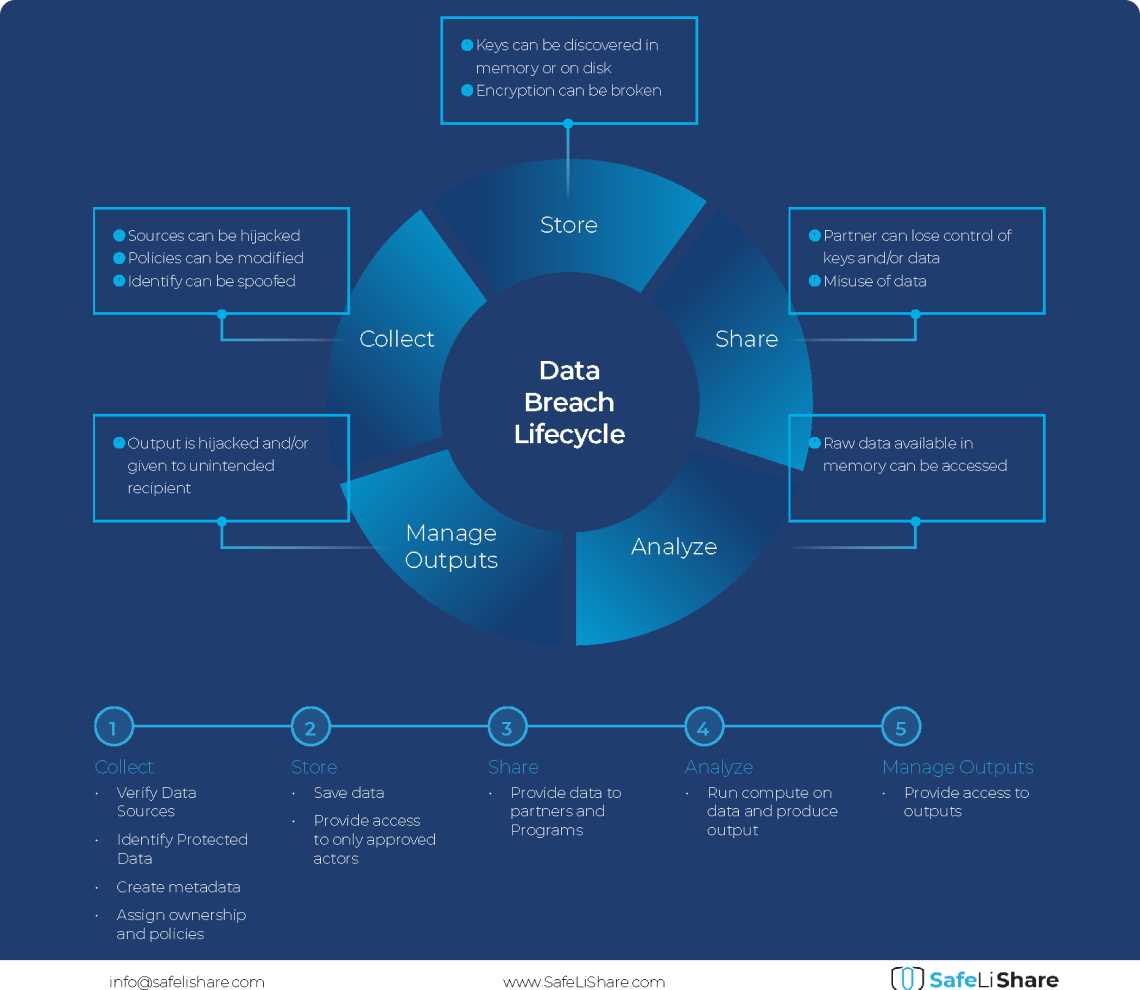
Cloud Data Breach Lifecycle Explained
During the data life cycle, sensitive information may be exposed to vulnerabilities in transfer, storage, and processing activities.

February 21, 2024
Bring Compute to Data
Predicting cloud data egress costs can be a daunting task, often leading to unexpected expenses post-collaboration and inference.

February 21, 2024
Zero Trust and LLM: Better Together
Cloud analytics inference and Zero Trust security principles are synergistic components that significantly enhance data-driven decision-making and cybersecurity resilience.